
- Automotive & EV▼
- IoT▼
- Digital Solutions▼
- Industries▼
- Technology▼
- Digital Growth Enablers▼
- Commerce & Experience Services▼
- Success Stories▼
- Thought Leadership▼
- Industries
- AI/ML▼
- Company▼
- Careers▼
- Contact Us
- Blog





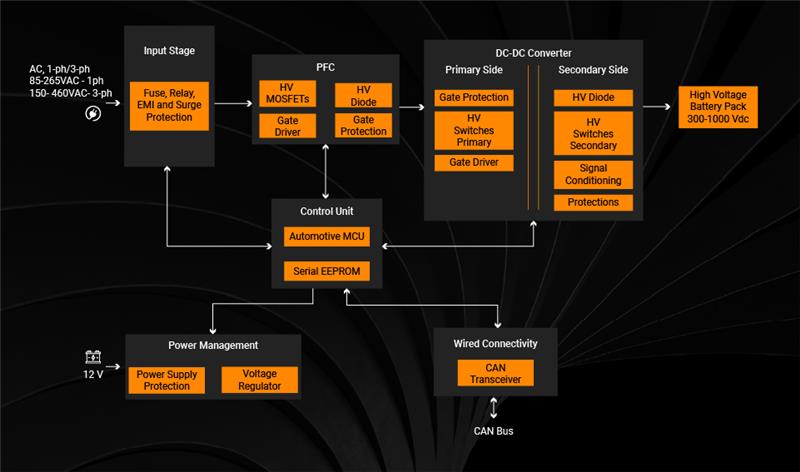
High-Performance AC-to-DC Conversion: The On-Board Charger (OBC) enables Battery Electric Vehicles and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles to draw power from standard AC sources, whether at residential, commercial, or public charging stations and converts it into the precise DC voltage and current required by the vehicle’s battery pack.
Integrated Safety & Intelligent Control: Modern OBCs are equipped with charge monitoring, thermal management, and fault-protection mechanisms, ensuring compliance with global safety and grid-interoperability standards (such as IEC and ISO).
Engineering Expertise that Delivers: With 19+ years of automotive engineering experience, Embitel provides custom-designed OBC solutions, from hardware and firmware development to power-conversion algorithms and validation. Our expertise supports seamless integration with diverse EV platforms while meeting stringent performance, reliability, and certification requirements.
Electrify Your OBC design. Connect with our experts today!




On-Board Charger communication protocols are essential for safe, efficient, and interoperable EV charging. They enable seamless data exchange between vehicles and chargers, optimize charging performance, and ensure grid integration.
Advancements such as ISO 15118, Plug-and-Charge, and bidirectional energy flow are shaping smarter, standardized charging ecosystems. As EV adoption accelerates, these protocols drive innovation, enhance user convenience, and support a more sustainable transportation future.

Electric Vehicle (EV) charging networks enable drivers to access AC and DC charging points at homes, workplaces, and public locations. AC chargers rely on the vehicle’s onboard charger for power conversion, while DC chargers deliver faster, high-power charging directly to the battery.
Embitel’s IoT-based Charging Station Network Solutions support operators with centralized monitoring, real-time station health checks, usage analytics, and secure installations. These solutions streamline network management, enhance reliability, and improve user experience for large-scale EV charging infrastructure.

Embitel offers end-to-end traction inverter and DC-DC converter solutions that power EV drivetrains with efficiency, safety, and precision. With expertise in FOC, SPWM, SVM algorithms, model-based development (MBD), and ISO 26262-compliant designs, our solutions support a wide range of motors and power ratings up to 30 kW.

EV charging protocols like CCS, CHAdeMO, and GB/T are redefining how electric vehicles connect safely and efficiently to charging stations. These standards ensure compatibility between EVs and charging equipment, enabling secure data communication, optimized power transfer, and reliable charging across global networks.
Yes, modern On-Board Chargers are designed for both Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), covering 2W, 3W, and 4W platforms.
To achieve a satisfactory Return on Investment, new On-Board Chargers need to be redesigned from the ground up. Various ceramics, such as Silicon Nitride or Aluminium Oxides, can serve this purpose, however, Aluminium Nitride (AlN) offers the highest thermal conductivity and thus the lowest heat resistance.
The primary distinction between an On-Board Charger and an inverter lies in their functions. While the inverter converts DC power from the battery into AC power to drive the electric motor, the charger performs the opposite task. It converts AC voltage into DC voltage to charge the battery in hybrid plug-in or all-electric vehicles
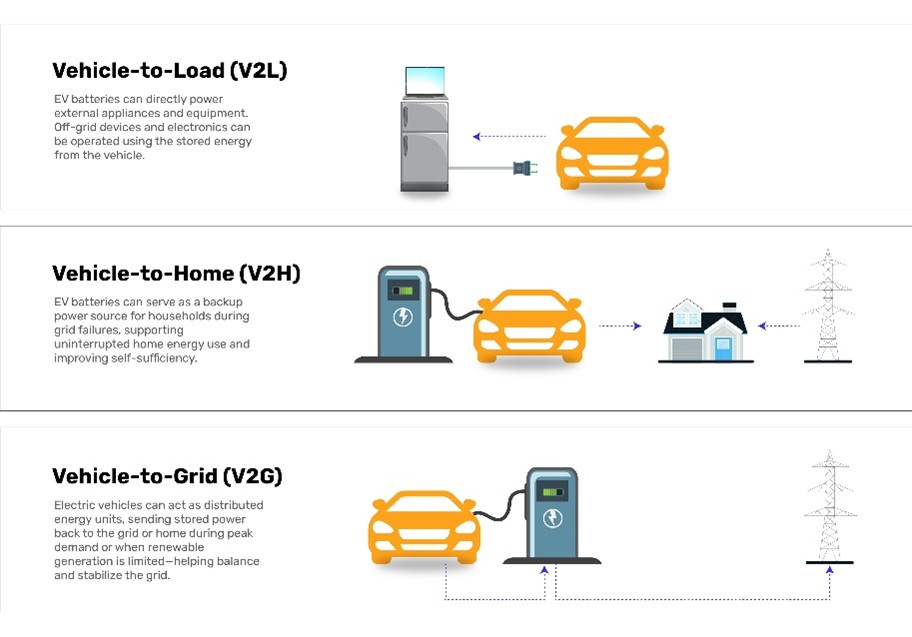
Bidirectional OBCs allow energy to flow from the grid to the vehicle (G2V) and back from the vehicle to homes, devices, or other vehicles (V2H, V2L, V2V), turning EVs into mobile energy hubs.
OBCs include charge monitoring, fault protection, thermal management, and compliance with global safety standards like ISO 26262 and IEC protocols.
A 2-in-1 combines the OBC and DC-DC converter in one unit, while a 3-in-1 adds a Power Distribution Unit (PDU), saving space, reducing weight, and simplifying integration.
Yes, modern On-Board Chargers support SAE J1772 (Type 1/2), CCS 1/2, and Bharat AC-001, ensuring compatibility with residential, commercial, and public charging infrastructure.
An On-Board Charger is an electronic device found in electric vehicles (EVs) that converts AC power from external sources, such as residential outlets, into DC power. This DC power is used to charge the EV’s battery pack.
Present day On-Board Chargers offer numerous benefits, including convenience, portability, efficient charging, and built-in safety features. Integrating the charger into the device eliminates the need for external charging equipment, enhancing convenience.
Efficient thermal management ensures components like SiC MOSFETs and inductors operate safely under high power, preventing overheating and improving reliability and lifespan.
High-performance On-Board Chargers can reach up to 96% efficiency, minimizing energy losses during AC-to-DC conversion while maintaining thermal stability.
They support wide AC input ranges: single-phase 85–265V, three-phase 150–460V, and DC outputs from 300V up to 1000V depending on the vehicle and system design.
Protocols like ISO 15118 and Plug-and-Charge enable smart data exchange between vehicle and charger, optimizing charging, enabling bidirectional flow, and supporting grid interoperability.