Functional Safety for Automotive ECU Development




The stakes for functional safety (FuSa) rise with every innovative feature added to vehicles. Whether it is ADAS, autonomous driving system, Electronic power steering or Brake ECUs, functional safety is paramount for all of them.
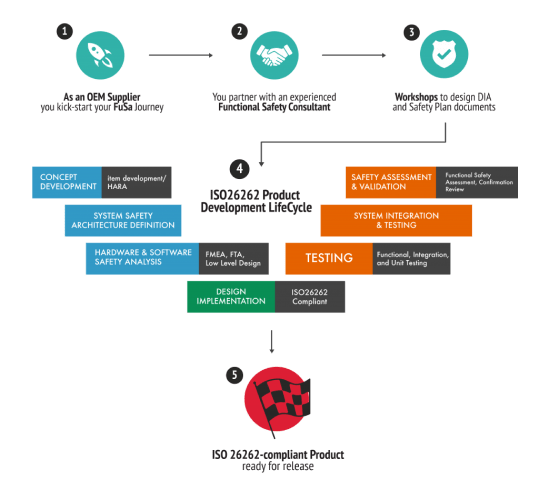
The proven approach to ensure functional safety is by following ISO 26262 standard. It ensures that functional safety is embedded in the development cycle through the concept phase, development and verification.
At Embitel, we are dedicated to help your automotive solutions meet ISO 26262 standard in letter and spirit.
With 16+ years of domain expertise in Automotive and in-depth know-how of Functional Safety implementation practices, we help you to deliver ISO 26262 compliant solutions for your customers.
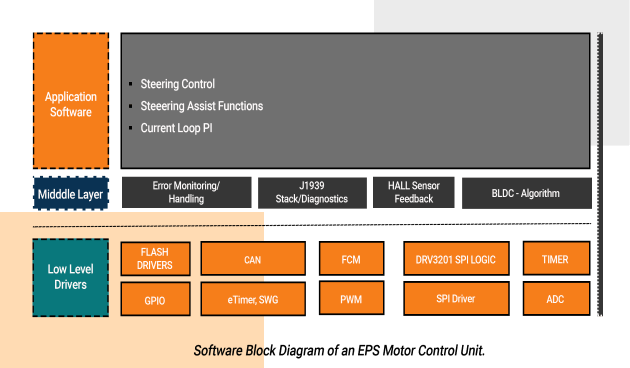
We have partnered with customers across Europe, Asia and US for development of various ASIL D compliant automotive solutions including Brake ECU, EPS ECU and more.
Automotive Functional Safety Success Stories
Our Functional Safety (FuSa) Service Offerings
Functional Safety Concept Phase
- Support for Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) and HAZOP analysis.
- Defining system-level safety requirements to address identified hazards.
- Establishing FuSa strategies to achieve safety goals.
- Allocation of safety measures across system components.
- Expertise in tools like DOORA, Polarion and JAMA tools.
Functional Safety Engineering
- ISO 26262 consulting services
- Tool Qualification
- Safety Element Out of Context development.
- Design of software and hardware architectures ensuring non-interference and ASIL decomposition.
- Gap analysis at technical and functional levels.
- Model based development using tools- MATLAB, SIMULINK etc.
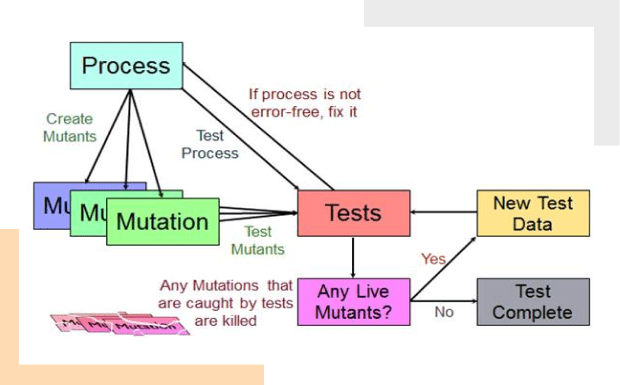
ISO 26262 Compliant Testing Strategies
- Static analysis with Polyspace, Helix QAC, and LDRA for MISRA and ISO 26262 compliance.
- Unit, integration, and system tests using VectorCAST, Tessy, and Cantata.
- Fault injection testing with Synopsys TestMAX, Razorcat TESSY, and NI TestStand.
- HIL and SIL validation using dSPACE, ETAS LABCAR, and Simulink Test.
- Traceability management with Jama Connect, Polarion, and DOORS.
Safety Analyses
- Software and Hardware Failure Modes & Effect Analysis (FMEA).
- SPFM, LFM and PMHF Derivation using FMEDA.
- Fault Tree Analysis and Dependent Failure Analysis.
- Expertise in tools like Medini Analyzer, Enco SOX tool.
Functional Safety Supporting Processes
- Support for configuration and change management.
- Support for ISO 26262 documentation: Development Interface Agreement (DIA), Safety case, Hardware-Software Interface and other documents.
- Safety case documentation to support certification and assessment processes.
Functional Safety Management
- Design of modular documentation structures for safety artifacts.
- Implementation of end-to-end traceability across requirements, designs, and tests.
- Development of detailed activity plans aligned with the product lifecycle.
Your Functional Safety(FuSa) Journey:
How do we Ensure FuSa Compliance for Automotive Systems

Comprehensive ISO 26262 and FuSa Expertise

Comprehensive Safety Analysis

End-to-End Functional Safety Support

Proven Track Record and Tools
Handbook: Functional Safety (FuSa) Consulting Services
Get more details about our service offerings for the implementation of ISO 26262 based FuSa framework for Automotive Projects
[Video on ISO 26262] How to Derive Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) Using HARA
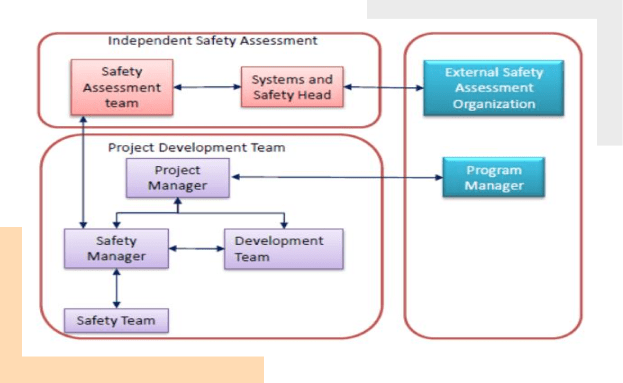
Functional Safety Consultants: Team Structure
01
Veteran Functional Safety Managers
who partner with you to achieve compliance with the desired ASIL Grade (ASIL B, ASIL C or ASIL D)
02
Senior ISO 26262 consultant
with 20+years of experience, to partner with you for critical automotive projects for product development and consulting support
03
Senior embedded engineers
Proficient in developing automotive applications as per the latest industry standards including AUTOSAR, ISO 26262 and MBD.
Download Webinars: Learn more about ISO 26262 standard and Functional Safety in Automotive
- Webinar on How to re-use software modules in compliance with ASIL (ISO 26262 standard)
- Webinar on Software development according to ISO 26262
- Webinar on Introduction to ISO 26262 for Functional Safety Critical Projects
- Making ‘Functional Safety’ a Part of Your Organization DNA
- Webinar: How to Evaluate Hardware Architecture Metrics for Automotive ECUs (Using FMEDA Method)
FAQs’:ISO 26262 Consulting, Analysis and Design/Development Services
Knowledge bytes
What is Functional Safety in Automotive? What is the role of ISO26262 Standard?
A number of components of a car are safety critical; like,
Electronic Steering System, Anti-lock Braking System, Air-bags, electronic stability
control, and more.
By safety critical, we mean that the failure of these components
can risk the driver or the passengers’ life.
ISO26262 is a standard that defines a
framework to implement safety practices during the design, development, and the testing of
all the critical electrical and electronic components of a road vehicle. This standard has
been derived from IEC61508.
ISO26262 standard comprises of a set of steps that
regulate the product lifecycle at the software and the hardware level. ISO26262 provides an
extensive set of recommendation for automotive product development, right from the
conceptualization to the decommissioning stage.
What is ASIL in Automotive Functional Safety?
A number of components of a car are safety critical; like,
Electronic Steering System, Anti-lock Braking System, Air-bags, electronic stability
control, and more.
By safety critical, we mean that the failure of these components
can risk the driver or the passengers’ life.
ISO26262 is a standard that defines a
framework to implement safety practices during the design, development, and the testing of
all the critical electrical and electronic components of a road vehicle. This standard has
been derived from IEC61508.
ISO26262 standard comprises of a set of steps that
regulate the product lifecycle at the software and the hardware level. ISO26262 provides an
extensive set of recommendation for automotive product development, right from the
conceptualization to the decommissioning stage.ASIL (Automotive Safety Integrity Level) is
the notation for software or hardware component that signifies its safety-criticality.
ASIL has four categories- ASIL A, ASIL B, ASIL C, and ASIL D. ASIL A indicates least
critical level and D indicates the most critical level. There are three factors that
determine the ASIL of a software or hardware- probability of exposure, controllability by
the driver, and the severity of the outcome if a fault occurs.
ASIL A is almost
equivalent to QM level, therefore, ASIL B is usually the minimum requirement, in order to
make your product complaint with ISO 26262 Standard for Functional Safety.
Considering the example of an Air-Bag, the analysis will look into how likely it is
for the air bag to get activated, what will be the effect on car and how can the driver
control it. Considering all these factors, ASIL will be determined, which will most likely
be ASIL-D for Air- Bags.
ASIL is determined at the beginning of the automotive
software development with the help of HARA. However, it can be done post the development
also, but is not recommended. Based on the ASIL rating, safety processes and testing
regulations are followed- strictest for D and flexible for A.
Functional Safety Webinars and Articles
- Understanding How ISO 26262 ASIL is Determined for Automotive Applications
- Challenges Your Automotive Team may Face in ISO 26262 Functional Safety Compliance
- Understanding the Automotive Functional Safety Best-Practices with ISO 26262 standard
- Why ‘Safety Plan’ is Critical in Development of ISO 26262 Complaint Product and Automotive Functional Safety
- ISO Compliant Unit Testing Strategies: A Step Towards Achieving Functional Safety in Automotive Product Development
- [Video] How ASIL is Determined for Automotive Applications as per ISO 26262 Standard
- [Vlog – ISO 26262 Standard for Functional Safety] How to Evaluate Hardware Architecture Metrics Using FMEDA Method
Related Blogs: Learn more about ISO 26262 Functional Safety
- What is ISO 26262?
- Understanding How ISO 26262 ASIL is Determined for Automotive Applications
- Challenges Your Automotive Team may Face in ISO 26262 Functional Safety Compliance
- Understanding the Automotive Functional Safety Best-Practices with ISO 26262 standard
- Why ‘Safety Plan’ is Critical in Development of ISO 26262 Complaint Product and Automotive Functional Safety
- ISO Compliant Unit Testing Strategies: A Step Towards Achieving Functional Safety in Automotive Product Development
- [Video] How ASIL is Determined for Automotive Applications as per ISO 26262 Standard
- [Vlog – ISO 26262 Standard for Functional Safety] How to Evaluate Hardware Architecture Metrics Using FMEDA Method