Automotive Cybersecurity : Solutions and Services
Automotive cybersecurity is the practice of protecting vehicle systems, electronic control units (ECUs), and in-vehicle networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks that could impact safety, performance, or privacy.
Automotive cybersecurity goes beyond traditional information security.
It bridges compliance requirements such as ISO 21434 (road-vehicle cybersecurity engineering), ISO 27001 (information security), and GDPR (data privacy).
Together, these frameworks ensure that both vehicle systems and customer data remain secure across the entire product lifecycle.
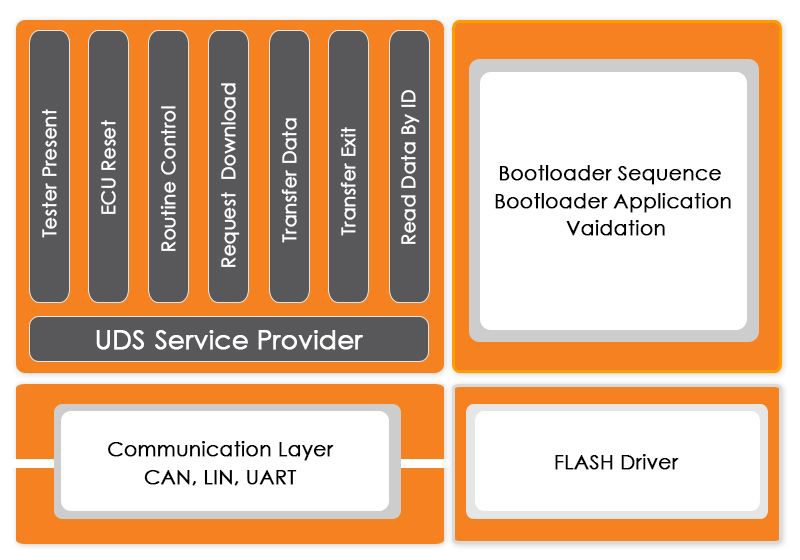
We at Embitel, have delivered multiple automotive projects with cybersecurity at their core. So, we know where to put the plug! Automotive cybersecurity is all-pervasive, hardware, software, network, and cloud; we help you secure each one of them. From building secure bootloaders and Transport layer security to Trusted Applications for automotive cybersecurity and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) services , we implement cybersecurity in all its forms.
Secure Your SDV Today