As we progress into the domain of automotive cybersecurity and connected vehicles, choosing the right security mechanism remains a constant topic of debate. Widely used in most vehicles today, TEE and HSM are considered among the most efficient security solutions.
But which one is best? Let’s understand with practical evidence.
Traditionally used in automotive applications for years, Hardware Security Module (HSM) has always been a reliable solution to ensure the vehicle’s safety and security.
However, as we rapidly advance, the automotive industry is gradually moving towards self-driving cars and interconnected automobile devices. Undoubtedly, these new developments are not just futuristic and innovative but also bring with them security vulnerabilities.
In the last few years, Trusted Execution Environment, aka TEE, has emerged as an efficient solution that aims to provide advanced security solutions to tackle the evolving threats.
While its primary aim is the same as that of HSM, it significantly differs in architecture, functioning, performance, and cost.

How Security Mechanisms Work in Automobiles
Before we dive in and understand the fundamental differences between the two security mechanisms, it’s important to understand why we even need them in the first place.
Suppose you want to unlock your car with your phone. While the request looks simple and executes in a matter of a few milliseconds, a lot goes on behind the scenes.
To break this simple process, your phone first sends a digital key (request) to your car to unlock your vehicle, which is then received by the operating system of your car and is forwarded and verified by your car’s security mechanism and processed only if the request is valid.
Sounds complex, doesn’t it?
Well, it is; to perform such critical functions or similar requests that require key validation, the car’s operating system puts in use cryptographic keys that carry sensitive data, making them prone to cyberattacks.
Purpose of TEE and HSM in Automotives
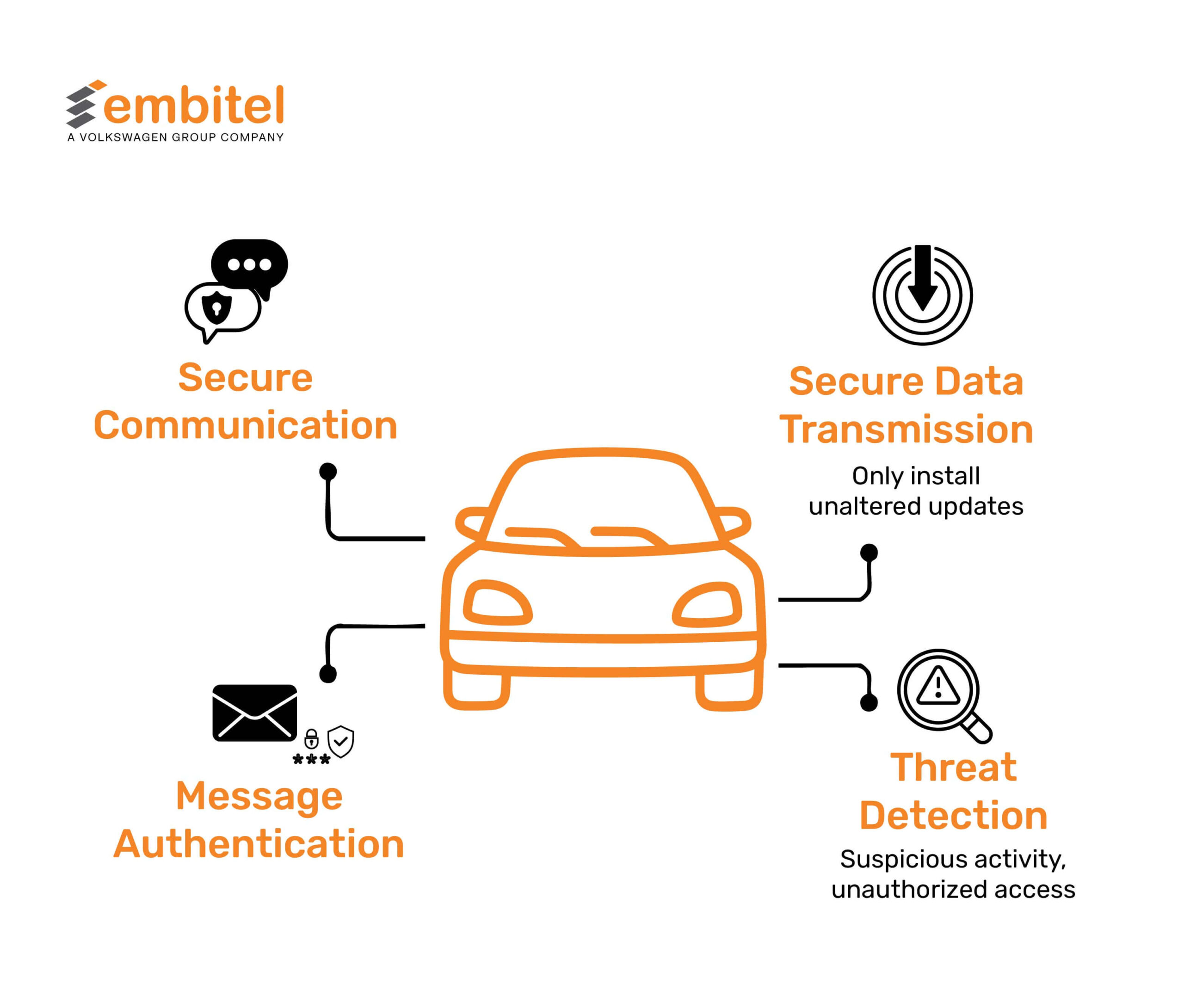
Automotive Security mechanisms like HSM and TEE function to ensure the safety and security of these cryptographic keys and perform other critical functions like
- Enabling secure communication in vehicles, Controlled Area Network (CAN),
- Secure data transmission to make sure the vehicle only installs unaltered updates, i.e., over-the-air (OTA) updates from the manufacturer,
- Validation and authentication of messages received from other vehicles and networked devices.
- Detection and prevention of suspicious activity and unauthorized access.
HSM Vs TEE: Key Differences in Automotive Applications
Now that you might have a clear idea of how the security mechanisms operate within automotives, let’s delve in and understand the difference between HSM and TEE.
| TEE (Trusted Execution Environment) | HSM (Hardware Security Module) | |
| Architecture | Software-based, embedded in main processor (SoC) | Separate hardware module within ECU |
| Functionality |
Provides logical isolation for secure code execution and data operations |
Provides a wide range of cryptographic services including key management, encryption, decryption, digital signing, and secure data handling |
| Placement | Inside the main SoC, alongside the REE | Dedicated microcontroller in the ECU, separate from main processor |
| Performance | General-purpose secure environment; limited resources for cryptography | Optimized for high-speed cryptographic operations like RSA, signing |
| Tamper Resistance | Secure but not physically tamper-resistant | Highly tamper-resistant; can wipe data during breaches |
| Cost | Cost-effective; no additional hardware required | Higher cost due to dedicated hardware and certifications |
| Use Cases | Secure execution of trusted apps, key protection, and authentication | Key storage, OTA updates, secure boot, and communication verification |
| Origin | Derived from mobile device security (e.g., ARM TrustZone) | Traditional security module in automotive and enterprise applications |
While the distinction table gives you only a brief overview of the differences in both security mechanisms, let’s understand each of their aspects in detail.
Differences in the Architecture of HSM and TEE
HSM, which stands for Hardware Security Module, is a microprocessor that manages and stores cryptographic keys and handles the execution of sensitive data operations.
In simple words, HSM, as its name suggests, is a hardware device designed to ensure the physical and logical protection of keys and certificates in a system. In addition, it also encrypts and decrypts sensitive data, offering a tamper-resistant environment.
On the other hand, TEE, or Trusted Execution Environment, works like a pre-integrated secure folder in the computer’s main operating system. It is implemented as a logically separate environment within the vehicle’s processor.
Unlike HSMs, it is not a separate hardware; it rather offers a trusted environment on the System on Chip (SoC), capable of executing sensitive operations.
The TEE mechanism primarily originated from its use in Android devices, which is used to store, process, and secure the integral keys and certificates present in the same processor of the device of your mobile phone.
How HSM and TEE Function in Automotives
When it comes to functioning, HSMs are placed within the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) in automotive applications that work separately from the main car computer.
Generally, the main computer of a car handles routine operations like playing music and operating the AC. The HSM manages security operations and safeguards the vehicle’s main system against unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
Furthermore, in case of a security breach, HSM remains tamper-resistant; if someone tries to forcefully access data, its mechanism enables it to wipe out all personal data within.
The TEE mechanism also works similarly to HSM; it basically provides a secure area isolated from the main processor, aka REE (Rich Execution Environment), and allows Trusted Applications (TA) to execute sensitive operations like cryptographic processes, secure storage, and key authentication.
This isolation keeps attackers from taking advantage of OS or other application vulnerabilities to access protected data or code inside the TEE. Also, if the normal operating system of a vehicle device is violated in any way, then the data and processes in the TEE remain secure and protected.
While the HSM mechanism is efficient, it has its restrictions. It comes with a specific set of limited functionalities; for the technology to update, users can only upgrade by replacing the hardware module.
On the contrary, TEE, being a software-based mechanism, resolves this challenge with its structural build and functionality. It is flexible and can receive OTA updates, key management updates, and algorithm changes.
Performance Comparison
When talking about performance, HSMs act like special-purpose hardware that is optimized for cryptographic functions such as
- Key generation,
- Encryption and decryption of data
- Signing and verification of certificate authorities.
Additionally, it is also capable of performing cryptographic functions at high speeds, sometimes even higher than the performance of software implementations or general-purpose processors.
Furthermore, HSMs perform asymmetric key operations like RSA signatures and encryption with ease, which are most typically used for digital signatures and secure communication.
Conversely, TEEs offer a trusted environment for running code and securing data, but are not specifically geared towards high-performance cryptographic processing.
They are generally more concerned with general secure execution and might not support specific performance for particular cryptographic algorithms. Additionally, TEEs might possess scarce resources (CPU, memory) relative to HSMs, affecting their efficiency for cryptographic operations.
Cost Comparison
In terms of cost, HSMs are comparatively more expensive than TEEs, as they need dedicated hardware, which requires additional manufacturing costs.
Moreover, they also require automotive cybersecurity certification like FIPS 140-2 or Common Criteria, which adds to their cost of manufacturing.
On the other hand, TEEs are software implementations inside the primary processor and are pre-integrated in the SoCs, due to which they do not require any additional cost of manufacturing, making them cheaper.
Can TEE and HSM Function Together in Automotive Applications?
While the clear distinction between these factors distinguishing between TEE and HSM might have already helped you conclude what technology could be best suitable and sustainable for you.
However, despite different functioning methods and performance specialties, it’s noteworthy that TEE and HSM can coexist and function together in automotive applications.
Using both security mechanisms together can act like a double layer of security for the security of automobiles. Where can HSM be used to perform tasks like
- Encryption, decryption, digital signing, and key generation
- Secure storage, management, and protection of cryptographic keys
- Meeting regulatory compliance and security infrastructure management
While TEE can be used for
- Creating a secure environment to execute code and process data.
- Managing in-vehicle payment processing systems, i.e., toll collection, parking payment, etc.
- Setting up Driver Rights Management (DRM) features like Driver Authentication and Biometric Verification
FAQ
What is the difference between TEE and HSM?
TEE can be defined as a secure folder within the main processor of a device, offering logical isolation that enables a safer environment for code execution, while HSM is a separate hardware module that offers physical security of cryptographic keys and functions in automotive systems.
What is HSM in automotive?
An HSM in automotive is a hardware-based security module embedded within a vehicle’s ECU. It manages cryptographic keys, secures software updates, verifies communication, and prevents unauthorized access or tampering to ensure vehicle system safety.
What is the best TEE to use?
The ARM TrustZone is widely used in automotive and mobile devices as a recommended TEE. It offers robust security, industry support, and seamless integration with existing processors.
What is the difference between TEE and REE?
TEE (Trusted Execution Environment) is a secure, isolated area within a device’s processor for handling sensitive operations. REE (Rich Execution Environment) is the main operating system that runs general applications but is more vulnerable to threats.
Wrapping Up
Both TEE and HSM serve the same purpose to secure the cryptographic keys and data operations in automobile applications, with different architectures.
Undoubtedly, each of the security mechanisms has its specific benefits under different factors. The application of the right mechanism is quite dependent on your requirements, whereas the application of both mechanisms can assure double security and offer enhanced vehicle security.



