Transportation from point A to B is a fundamental aspect of human life, and hence, automobiles remain essential. We live in a world where energy is scarce and pollution is everywhere. The need of the hour is a solution that will enable automotive sustainability - one that will address challenges such as carbon emissions and climate change, while discovering reuse/recycle opportunities in the automotive value chain.
This article directs the spotlight on an unsung hero of the automotive industry, telematics - quietly serving its purpose of making the automotive industry sustainable by:
- Reducing vehicle emissions
- Extending the automobile's life through predictive maintenance
- Enabling vehicle tracking to ensure safety
- Tracking performance to increase fuel efficiency
- Managing fleet efficiency
Goals to Attain Automotive Sustainability
In 2015, The United Nations Member States adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Out of these 17 Goals, SDG 12 – Ensure Sustainable Consumption and Production Patterns and SDG 13 – Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts hold great importance to in inching closer towards automotive sustainability.
SDG 12 - Ensure Sustainable Consumption and Production Patterns
- Target 12.2 in SDG 12 indicates the member states' agreement to achieve sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
- Target 12.5 aims towards substantially reducing waste generation through prevention reduction, recycling, and reuse.
SDG 13 - Take Urgent Action to Combat Climate Change
- Target 13.3 identifies the need for education, awareness-raising, and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning.
- Target 13.2 stresses integrating climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning.
From SDG 12 & 13, we understand the growing need to adopt measures to curb pollution and erratic resource consumption to avoid impending doom.
An industry that is evolving for the betterment of our environment by constantly integrating innovations is the automotive industry. Let’s explore the first step towards applying automotive sustainability initiatives.
Data Collection – The Backbone of Automotive Sustainability Initiatives
Telematic devices generate heaps of meaningful data. The commonly known telematic devices are Onboard diagnostic devices (OBD), Tachograps, Driver smartphones, and Black boxes.
Data generated through these devices is used by automotive manufacturers, insurance providers, and fleet managers. By analyzing the data, one can fine-tune their products to align with the goals linked to automotive sustainability.
Using telematic reports generated by the automotive industry, local governing bodies, national governments, auto insurance providers and fleet managers respectively can:
- Gain insights into the mobility practices in the urban regions most prone to generate emissions. The parameters used to describe urban mobility are average speed, traffic flow, travel time, frequency of travel during different hours of the day, vehicular emissions, travel demand, and access to public transport.
- Construct better roads and infrastructure to reduce traffic congestion
- Calculate premiums based on driver behavior, as a higher premium will indirectly affect the driver behavior and promote safer driving practices.
- Analyse Fleet Idle Time, Signal Violations, G-Force in braking zones, driver attentiveness (through video telematics), unnecessary acceleration, total distance driven, and many more parameters to enable fleet sustainability.
Mitigating Emissions for Automotive Sustainability
A country or a company is carbon neutral if it takes part in sustainability initiatives to remove the CO2 it produces from the atmosphere. Attaining carbon neutrality or net zero emissions is a major talking point for leaders of the modern world in sustainability summits. With automobiles alone contributing up to 16.2% of global CO2 emissions, automotive sustainability initiatives are the need of the hour.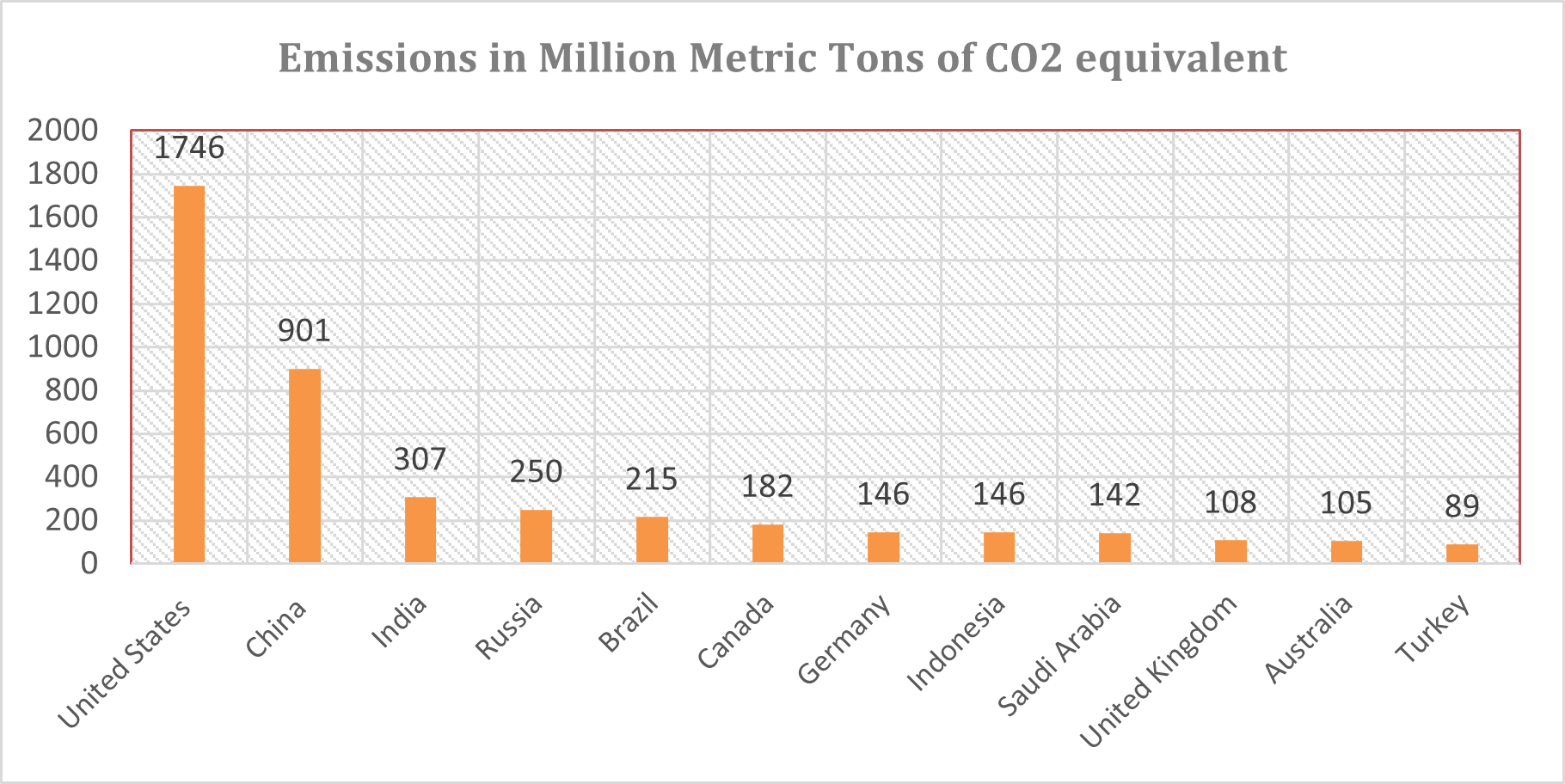
With vehicle emissions seen soaring as per Figure 1, economic powerhouses with technological capabilities need to set an example through automotive engineering for sustainable mobility.
Vehicle Telematics can play a huge role in enabling sustainability in the automotive industry in the following ways:
Route Optimization
- Communication channels such as V2V – Vehicle to Vehicle and V2E- Vehicle to Everything has made route optimization possible!
- With distance and time being the critical factors in deciding the best route for travel, telematics can help drivers in decision-making.
- These decisions help manage fuel consumption by reducing the overall distance traveled.
- Telematics, backed by AI/ML aids drivers in making dynamic adjustments to their preferred journey routes by considering factors such as traffic fluctuations, accidents, and road closures.
- Fleet managers can generate reports on the vehicle's environmental performance and provide the driver with suggestions on appropriate corrective actions, promoting fleet sustainability.
Idle vehicle – An air pollution workshop
- Idling is a noteworthy culprit in emitting large amounts of emissions.
- Vehicles stuck in traffic jams and red lights contribute up to 40% more pollutants than vehicles that are moving.
- Idling automobiles alone contribute up to 30 million tons of CO2 annually in the US alone.
- An ideal solution to this is turning off the engine after 10-12 seconds of idle time as restarting the vehicle utilizes the same amount of fuel required for it to stay in the idling condition.
- Private vehicle owners can retrieve idling reports to identify if excessive fuel is being wasted.
- As fleets heavily invest in fuel for operations, tracking driver behavior to curb unnecessary idling will result in a reduction in operating costs and pollution and promote fleet sustainability.
Expanding Product Lifecycle for Automotive Sustainability
From a sustainability perspective, the age-old practice of servicing vehicles based on mileage and time is not ideal. Replacing components is expensive for both the customer and the environment.
Leveraging predictive maintenance, owners and fleet managers will now be aware of the health of each of their vehicle’s components. Staying on top of your automobile’s health leads to early detection of problems that can be fixed with minor tune-ups.
Onboard diagnostics hardware has gained a significant reputation as a sustainability enabler as it assists in:
- Shifting from scheduled to timely and on-demand assessments.
- Enabling vehicle owners to assess vehicle conditions when they choose.
- Facilitating timely intervention to address emerging issues.
In return, the automotive sustainability initiative:
- Reduces material wastage.
- Mitigates the environmental impact linked to scrapping the replaced components.
- Alignes with the global effort to conserve resources.
By enabling timely intervention OEMs can successfully utilize automotive engineering for sustainable mobility.
Vehicles can cut down on additional emissions produced by problematic components and extend the life of their assets. Apart from cutting down on emissions, predictive maintenance reduces material waste by extending component life by early identification of the problem.
Sustainability Initiatives Adopted by Automotive OEMs
Several OEMs across the world have pledged to play their part in converting the industry to a sustainable one! Take a look below and find out the trending automotive sustainability initiatives:
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) – By performing LCA analysis, automotive OEMs can study the environmental impact of their product across its entire life cycle. A fruitful LCA study will lead to altered production processes, material selection, sourcing, and end-of-life activities. These assessments are highly sought after to initiate practices that promote automotive sustainability.
- Targeting Net-Zero CO2 by 2040 - In the automotive industry, there's a clear trend towards considering the broader life-cycle CO2e impact. Particularly in Europe, OEMs are encouraging their supply chains to commit to CO2e targets well ahead of regulatory requirements. By 2025, mandatory CO2e labeling and reporting on product levels, along with maximum footprint thresholds, will be enforced.
- Evaluating the carbon footprint of all automotive technology choices at every stage of the life cycle - Although the production of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) may initially emit more CO2e than conventional vehicles due to resource extraction and energy-intensive manufacturing, there's potential for significant improvements through optimized mining and manufacturing techniques.
- Circular Economy (CE) – In the circular economy, resources are utilized sustainably, ensuring that materials are not discarded as waste and natural ecosystems are regenerated. This system focuses on keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible through practices like maintenance, refurbishment, and recycling.
There's optimism for increased CO2e data exchange between manufacturers, facilitating sustainability goals.
Additionally, the considerable GHG emission benefits during BEVs' use phase compared to traditional vehicles are recognized. While BEV efficiency is commendable, ongoing efforts are devoted to further enhancing sustainability.
It's essential to prioritize sustainability improvements across all components.
Keeping the production plant close to the material sourcing location is another way to reduce GHG emitted during raw material transportation.
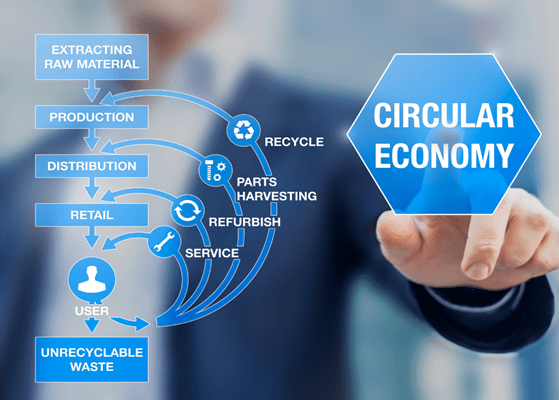
Fleets can effectively adopt these strategies to drive sustainability by enrolling themselves in recycling programs for a circular economy and integrating more EVs into their operations.
Telematics Solutions to Achieve Automotive Sustainability
In alignment with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, the automotive industry players are striving to achieve targets related to automotive sustainability i.e., sustainable consumption, efficient resource management, and urgent action against climate change.
By spreading awareness about these goals and fostering a culture of the above-mentioned eco-friendly practices, telematics and strategies become a catalyst for positive change.
The automotive industry, by embracing innovations and strategies discussed above, sets a precedent for a future where smart solutions are integral to reducing carbon footprints. With automotive sustainability initiatives steering us toward greener and safer roads, it's clear that technology, when harnessed responsibly, can be a driving force for a healthier planet.
Embitel has been at the forefront of developing custom Vehicle Telematics solutions. Contact our experts at sales@embitel.com to begin your Automotive Sustainability journey.


