As connected vehicle technology gets more and more advanced, the automotive engineering community has been making great strides in achieving the vision of autonomous driving. At the same time, vehicle HMI technologies have also been evolving at a fast pace.
The In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) systems in cars have reached a new level of sophistication, leading the way to digital cockpit solutions that promise a transformative driving experience. Rich OS designs and intuitive user interface for IVI systems are in great demand today. This is where Android Automotive comes into the picture.

Vehicle Infotainment System and Discontent Consumers
A survey conducted by Consumer Reports in 2019 assessed the satisfaction level of vehicle owners who used dashboard gadgetry. Insights from the survey findings pointed to widespread dissatisfaction in the usability of vehicle infotainment systems.
- High-end infotainment systems that are highly responsive and offered easy navigation through menu options received 86% owner satisfaction figures.
- Medium and low-end infotainment systems seemed to be more of a distraction for users, and garnered owner satisfaction rates in the range of 46%.
Vehicles equipped with Android Auto and Apple CarPlay use the data from the driver’s smartphone to access cloud-based services. This enables the driver to get real-time traffic details, better navigation advice and advanced speech processing capabilities. However, these smartphone-based systems are far from perfect.
The only other option for consumers is the built-in infotainment systems that run OEM proprietary applications. These built-in systems usually do not allow new features to be updated and third-party app integration. The survey results indicated that owners of vehicles with built-in infotainment systems showed the lowest satisfaction figures.
Difficulties that vehicle owners observed with these two types of infotainment systems are:
- Intermittent screen freezing while driving
- Difficulty toggling between Android Auto functions and those on the built-in system
- Phone-based navigation not possible when the phone signal or internet connectivity is weak
- Built-in infotainment systems not able to process voice commands easily
- Security considerations around the use of phone-based apps for mobility
The introduction of Android Automotive opens up a world of opportunities for OEMs to iron out these issues and offer better driving experiences.
Android Automotive OS and Its Benefits
Google’s Android Automotive is an Android operating system that is specifically tailored to be used in automobiles. Vehicle manufacturers have already started using the Android Automotive OS in vehicles. Polestar 2, the first electric vehicle powered by an Android Automotive OS, is soon expected to take the market by storm.
The vehicle infotainment systems of the past require a smartphone connection to provide navigation assistance through GPS or play media files.
On the other hand, Android Automotive OS enables the IVI system to perform all these functions without connecting to mobile devices.
|
Android Automotive makes it possible for drivers to download media apps directly onto the infotainment system, without having to connect to a mobile device. It also integrates infotainment functionalities with other automotive features (such as cabin climate control, charge level for EV, etc.) on a single user interface. |
Android Automotive OS offers a plethora of options to infotainment system development engineers and media app developers alike. The platform mitigates some of the biggest challenges faced by developers in the past.
- It enables screen size customizations, input methods and other OEM customizations.
- The platform also facilitates the implementation of regional guidelines for driver safety.
- The OS enables the use of Android open source platform for automotive applications. The versatility of the Android ecosystem and the consumer’s familiarity with the OS (owing to smartphone usage) can be harnessed and extended to the automotive experience as well.
- Android Automotive is evolving quickly to support an extensive range of functions for the IVI systems of tomorrow.
- OEMs can also choose to use Android Automotive and build their custom IVI system with third-party apps for navigation and VR, based on their unique requirements. There is no obligation to stick to standard Google services for navigation and VR.
- The existence of a large Android developer community is beneficial for IVI development engineers. Developers have easy access to a goldmine of information and reusable software from thousands of other Android developers.
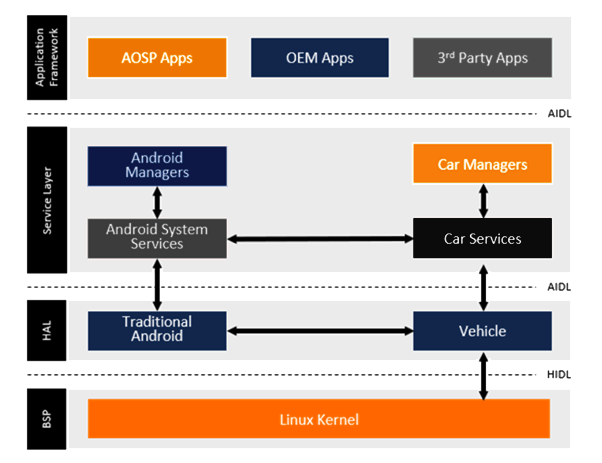
Android Automotive Architecture
A high-level architecture diagram of the Android Automotive OS is given below. It consists of the following generic components:
- Application Framework – This is also referred to as the HMI layer, and it contains the user and system applications. It is ideal to design applications in such a way that most of the core business requirements are moved to the Services layer. Such a design facilitates future scalability and easy updates.
- Android Automotive System Services – All System services are included in this layer. An interesting point to note is that OEMs can use the Services layer as a shield of security and avoid direct contact between the applications and the Hardware Abstraction Layer.
- Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) – The HAL exposes automotive interfaces to the system services in such a way that a vehicle-agnostic architecture is achieved. The application framework, System services and HAL are the core components of the Android Automotive OS platform, and these layers facilitate data exchange between vehicle ECUs and applications.
- Linux Kernel – Linux is the underlying kernel of the Android Automotive architecture.
Android Automotive Vs Android Auto
“Android Automotive” and “Android Auto” – The nomenclature here can certainly lead to confusions! Worry not; here is a simple explanation of how they differ:
- Android Auto – Android Auto literally lives on your smartphone, not on the automotive dashboard. You need to pair your mobile device to the vehicle’s infotainment system through a USB connection.
Let’s imagine a scenario where you are using a different car (compatible with Android Auto) each day. To have a consistent experience, you will have to pair the app on your phone with each vehicle’s infotainment system.
One of the main disadvantages of using Android Auto is the fact that it is powered by your mobile device. When travelling through an area with poor internet connectivity, you could experience irregularities in vehicle tracking.
- Android Automotive – As explained above, Android Automotive is a complete platform that has been developed solely to power automotive infotainment systems. This OS runs directly on the vehicle’s hardware, and there is no need for an external connection with a mobile device.
The Android Automotive OS supports apps that are developed for Android Auto as well. The platform can be easily customised by OEMs to offer unique experiences to consumers.
Google Automotive Services (GAS)
GAS is a consolidated set of services and applications that automotive OEMs can purchase from Google, while adhering to the licensing terms. These can also be integrated as is, with the IVI systems they are developing. Some of the services included in this bundle are:
- Google Assistant
- Precompiled wizard for Setup
- Google Maps and Navigation
- Automotive Keyboard
- Google Playstore
OEMs can choose to avoid the usage of the services and applications in GAS. They would then have to download the free version of the AOSP source code along with the relevant extensions to be used on their IVI systems. Subsequently, they can also integrate their own services and applications, based on their unique business requirements.
Embitel’s Android Automotive Development Experience
We have been partnering with global OEMs for the development of dashboard electronics for more than 14 years. One of our recent projects was for a US-based EV company developing a production line of futuristic SUVs.
The customer decided to opt for Android Automotive OS for their flagship SUV project. We designed and developed a high-end Infotainment Unit that includes functionalities such as navigation, vehicle condition display, Bluetooth connectivity, HVAC, driver and passenger seat temperature control, etc.
We also integrated FOTA update module and telematics functionality, while adhering to country-based GDPR guidelines. Learn more about this Android Automotive based IVI system development project here.
Conclusion
The consumer’s expectations from IVI systems are ever-increasing. This makes it inevitable for on-board capabilities of the vehicle to be integrated with the IoT Cloud. The advent of 5G and other wireless technologies will only fortify this connected architecture.
The result will be a new generation of powerful digital cockpit solutions at the hub of the vehicle cabin in the future. Android Automotive OS is created to cater to these software-defined platforms.
Connect with us at sales@embitel.com for transforming your IVI vision into reality. We help you in implementing Android Automotive on IVI systems across a multitude of hardware platforms and HMI frameworks. We can assist you in the end-to-end journey, right from the concept development to the application deployment and monitoring phases.


